Chapter 3 Running Programs
3.1 Learning objectives
Run UNIX commands
Wrap UNIX commands in a Bash script
Make a Bash script executable
Run a Bash script
3.2 Run UNIX commands
- Start a terminal
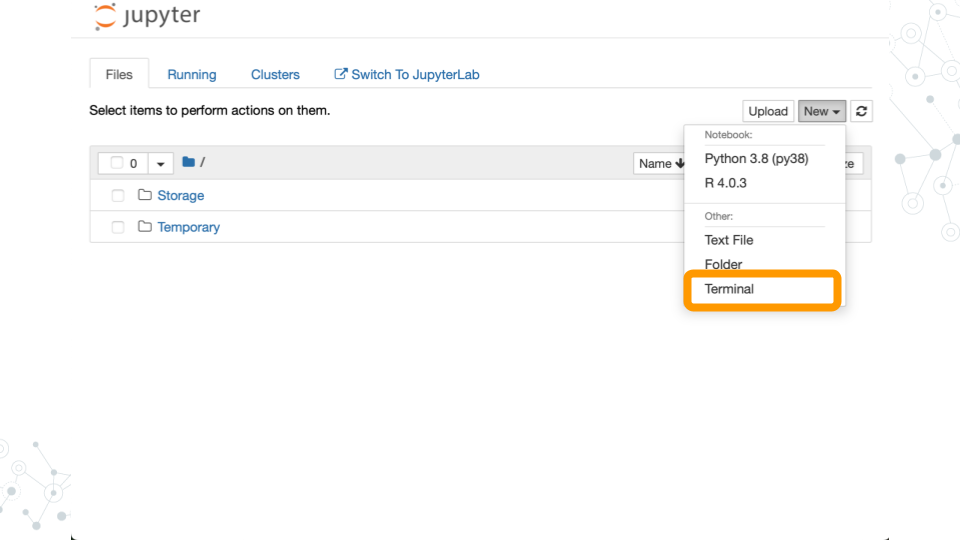
- Run the
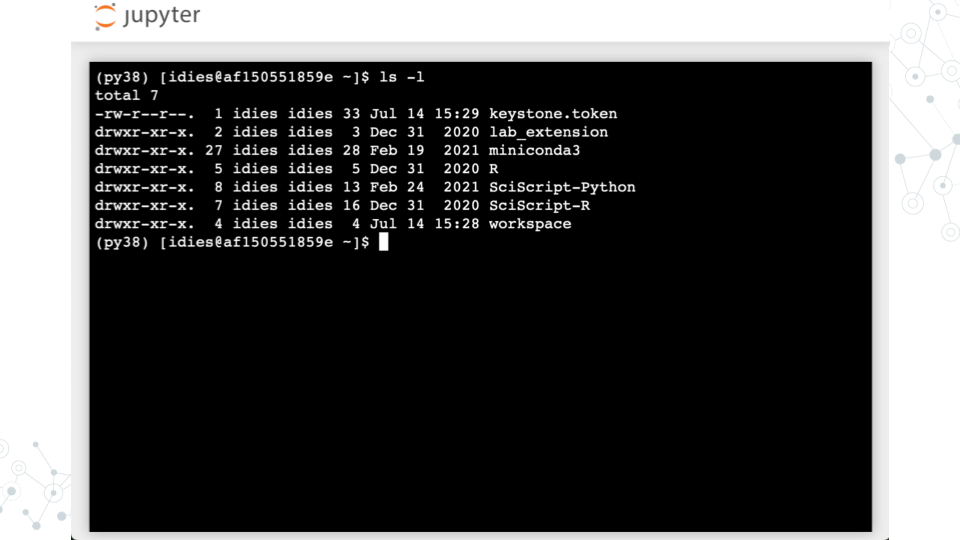
ls -lcommand to list files (the-lis a command line argument that instructs thelsprogram to modify its operation so that longer details are provided about each file)
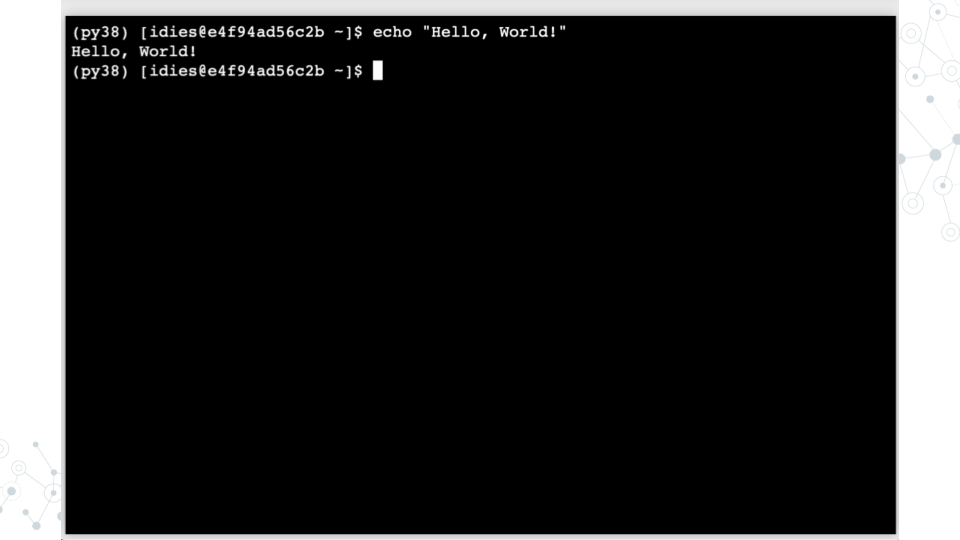
- Run
echo "Hello, World!"to print text to the terminal
3.3 Wrap commands in a Bash script
- Create Text File
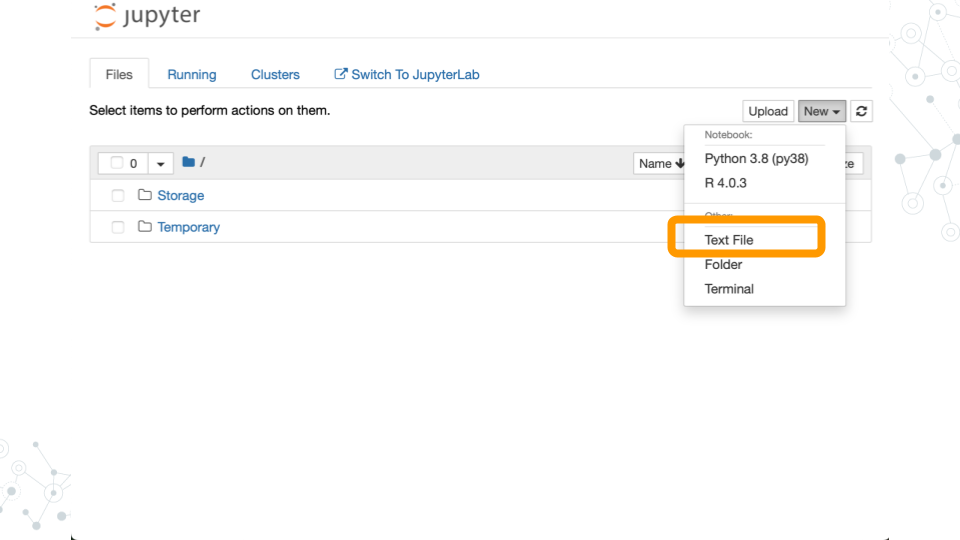
Write your first Bash script
- Add the following and save the file as
00-hello.sh
- Add the following and save the file as
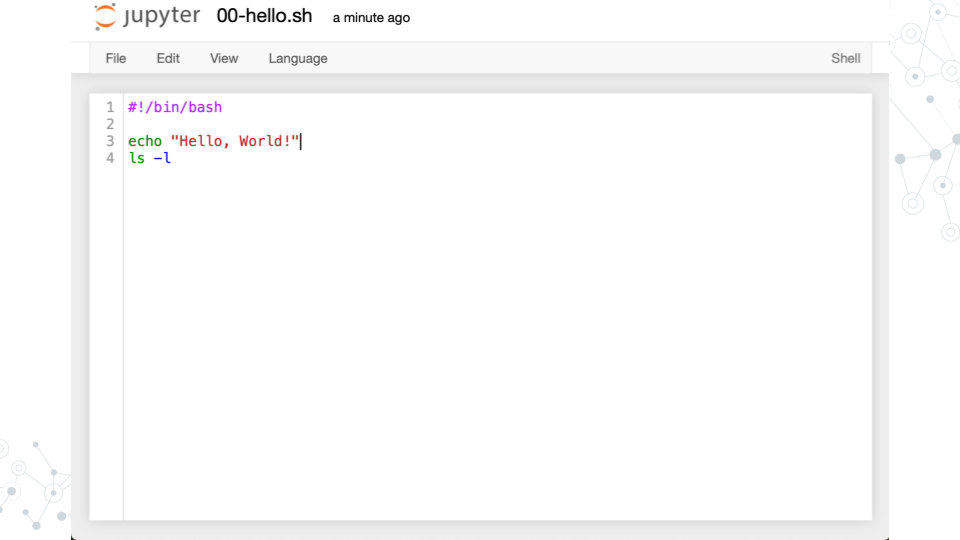
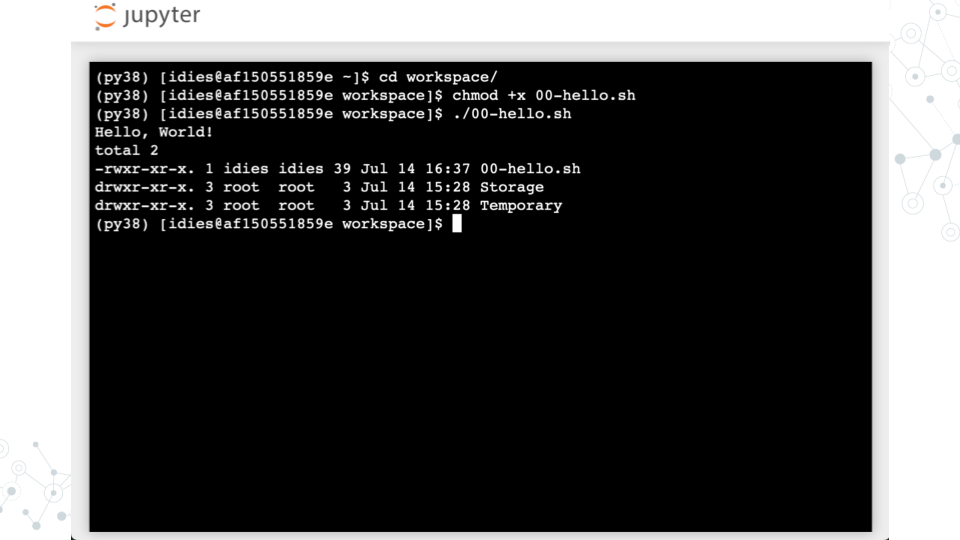
3.4 Run a Bash script
Now go back to the terminal:
- Change to the
workspacedirectory where you saved the file using thecdcommand
- Make the script executable using the
chmodcommand. This command changes the file permissions to allow execution (+x) of the script as a program
- Run the script by typing
./00-hello.shin the terminal: